Táboa de Contidos
Networking in Cloudstack
Introduction
When a network is created inside Cloudstack two things are created: a vlan is created to isolate this network from the other user's and a virtual router is also created to be the gateway to other networks, to be a firewall and to offer the nat service.
The external IP address of the router (which is in the 172.16.244.0/255 range) is reachable from any other ip address belonging to the CiTIUS network. Connecting to this ip address the user can reach all the VM created inside that network using NAT. Each network created will have a different IP address.
All VM receive their network configuration dinamically using DHCP without user intervention.
By default the virtual router is configured to block all communication between the external network and the user network. To open ports in the firewall and/or configure nat to allow VMs to reach the exterior networks you'll have to use the web interface as explained further ahead.
An example of two different user networks:
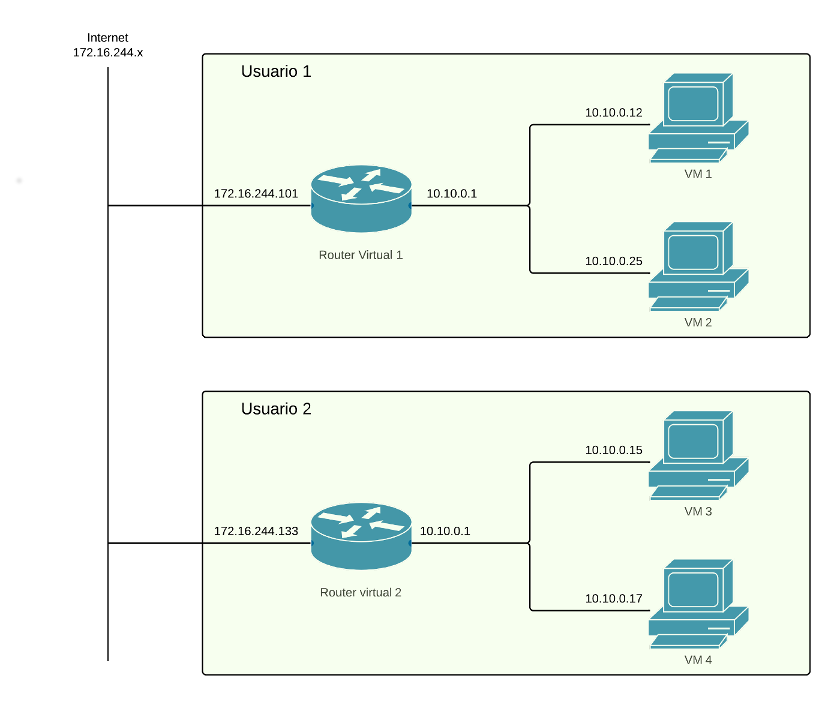
As you can see in the image user1 has created a network with two virtual machines, VM 1 and 2. This two VM can communicate between them because they are in the same network. Even though user 1 and user 2 networks have the same address range in their respective networks they belong to different vlans so are completely isolated between them. They can reach the external networks using the gateway of virtual router 1. This router has two network interfaces, one connected to the user network (10.0.0.1) and other to the CiTIUS network (172.16.244.101). User must connect to 172.16.244.101 to access any service offered by his virtual machines.
What determines to which service of which VM you connect to when accessing that IP address is whatever is configured in the NAT service of the virtual router. For example, supposing both VM1 and VM2 have web servers accessible at port 80 and that the router has the following nat rules configured:
Port 180 → port 80 of VM1
Port 280 → puerto 80 of VM2
then to access the first web page you should use 172.16.244.101:180 and to access the second 172.16.244.101:280.
Configuration
Configuration of networks in Cloudstack is done choosing “Network” in the left column:
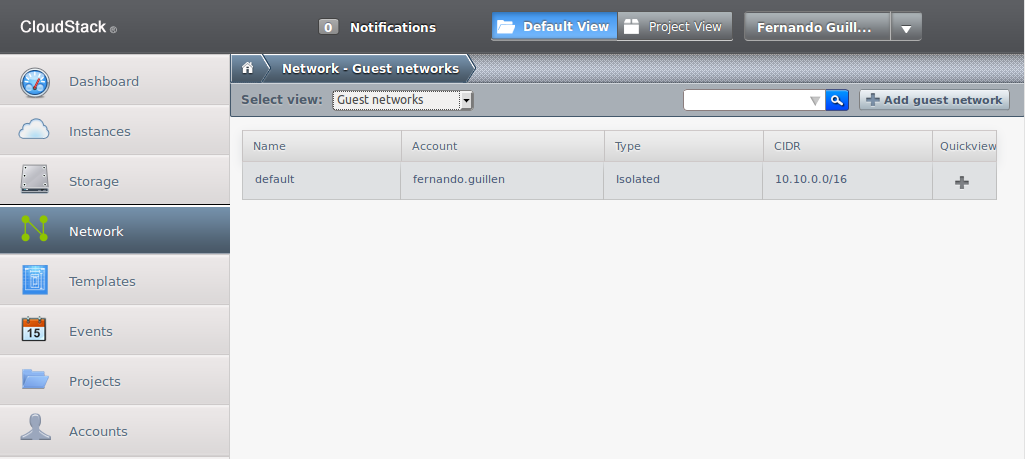
Here you'll see a list of the already created networks; in the previous example there is only one named “default”.
Create new networks
There are two ways of creating new networks, one automatic during the creation of a VM (recommended) and other manual by pressing button “Add guest network” located in the upper right part of the screen.
This will open a new window with a form to fill in the necessary data:
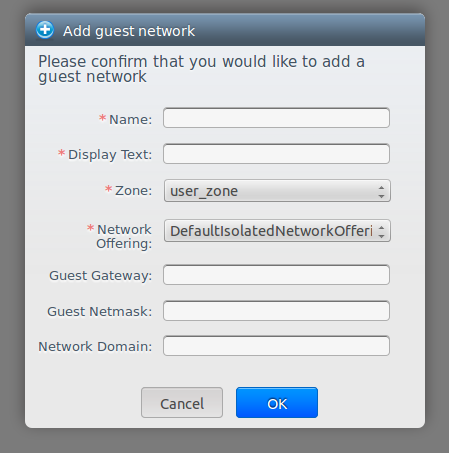
- Name: name of the network, Cloudstack does not use it, so choose something meaningful to you.
- Display text: Description, again only useful for the user.
- Zone: there is only one zone, leave it.
- Network offering: there is only one option, leave it.
- Guest gateway (optional): 10.10.0.1 by default, can be changed. It's the ip address of the internal network interface in the virtual router.
- Guest netmask (optional): network netmask.
- Network domain (optional): a domain name can be defined for the network.
Configure network
Choose a network and the following screen will appear:
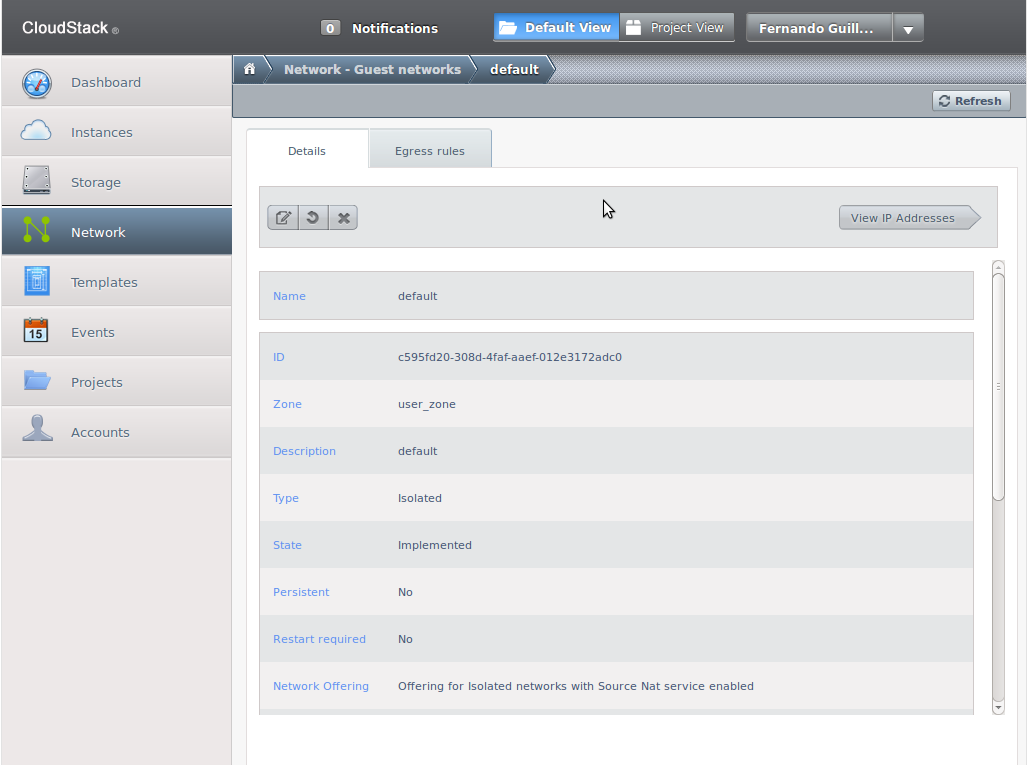
Here network two-way network traffic can be configured: from the VM to the outside and from the outside to the VM.
Configure access from the VM to the external network
By default the network firewall prevents any type of communication between the VM and the external network. To modify this configuration go to the “Egress rules” tab:
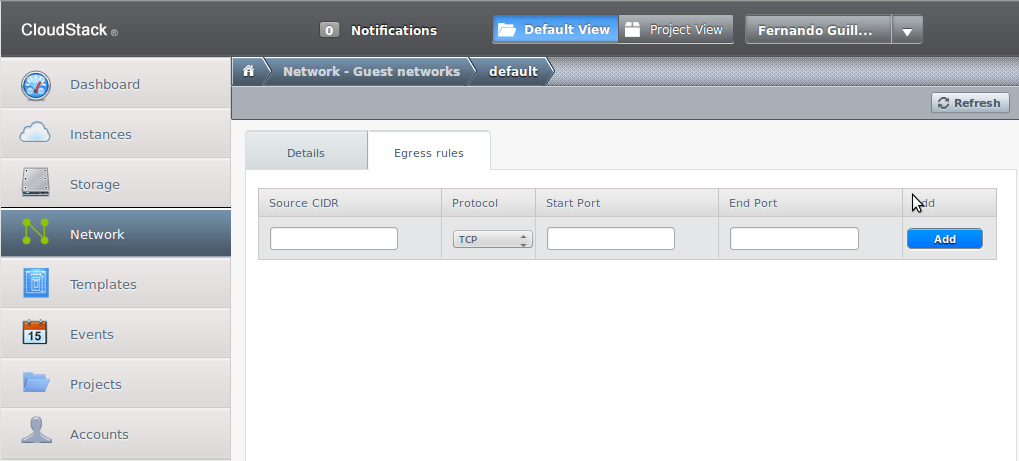
There a list with the current rules and a blank line for new ones appear. Rules work with implicit rejection which means that any traffic not explicitly allowed by a rule will be rejected. The simplest rule that can be added to allow all traffic from the VM to the exterior networks is:
| Source CIDR | 0.0.0.0/0 |
| Protocol | All |
CIDR 0.0.0.0/0 means any source and Protocol All means any port.
If less permissive rules are desired then put in the “Source CIDR” field the ip address of the host or network from which traffic is to be allowed and in the “Protocol”,“Start Port” and “Destination Port” fields the protocol and ports allowed.
Once the rule is created the “Add” button is substituted by a cross to allow its removal.
Configure traffic from the exterior to the VM
When a network is created two services are started in the virtual router: firewall and source nat. To allow trafiic from the exterior to reach a VM both services have to be configured. Firewall by default rejects all incoming traffic so explicit rules for any port desired to be open are necessary. Then Source nat configuration is required to direct that traffic to the desired VM.
To get to the configuration screen choose the netkwork name in the list, push the “View ip addresses” button and choose the networl ip address.
Choose the “Configuration” tab and you'll see the following screen:
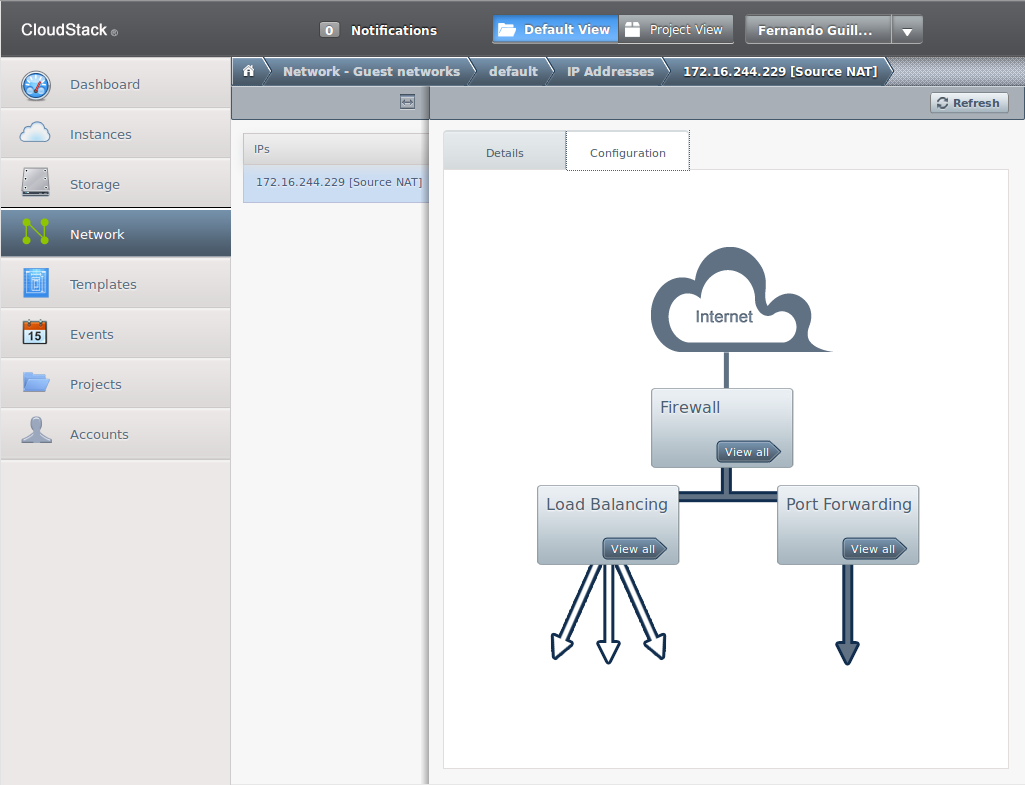
The “Firewall” and the “Port Forwarding” buttons open their respective configuration screens.
Configure the firewall
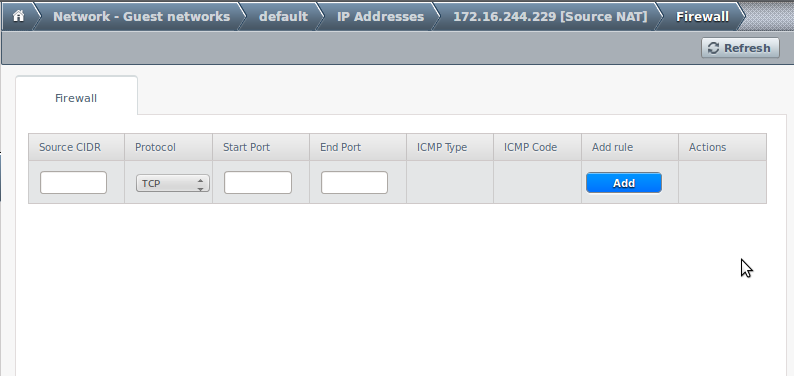
Here port ranges can be opened in order to be reachable form the external network:
- Source CIDR: from which source ip address traffic in this rule will be allowed. Can be a host, a network or 0.0.0.0/0 which means any.
- Protocol: TCP, UDP or ICMP.
- Start and End Ports (TCP and UDP only): define the port range to allow access. If a single port is needed put the same number in both.
- ICMP Type and ICMP Code (ICMP only): type of ICMP message allowed.
- Add rule: To add the rule to the list. Once added it is substituted by a button to remove it.
Configure nat
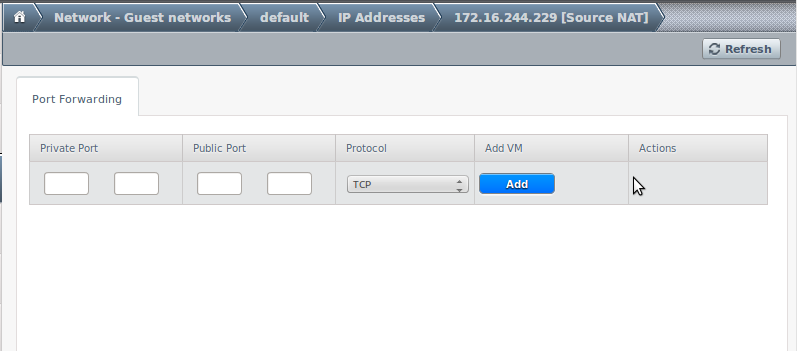
Here trafiic that reaches the external network interface of the router is redirected to a particular VM depending on the destination port number:
- Private port: port in the VM to connect to.
- Public port: port in the virtual router used to establish the connection.
- Protocol: TCP or UDP port.
- Add VM: choose the VM to which the connection will be redirected.